Trigonometry is the art of doing algebra over the circle. So it is a mixture of algebra and geometry. The sine and cosine functions are just the coordinates of a point on the unit circle. This implies the most fundamental formula in trigonometry (which we will call here the magic identity)
where
Example. Show that
Answer. By definitions of the trigonometric functions we have
Hence we have

Using the magic identity we get
This completes our proof.
Remark. the above formula is fundamental in many ways. For example, it is very useful in techniques of integration.
Example. Simplify the expression
Answer. We have by definition of the trigonometric functions
Hence

Using the magic identity we get
Putting stuff together we get

This gives

Using the magic identity we get
Therefore we have
Example. Check that
Answer. Use the definitions of the trigonometric functions to get
Hence we have
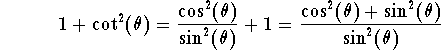
Using the magic identity we get
This completes our proof.
Example. Simplify the expression
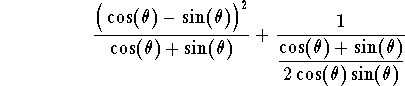
answer. Using algebra, we have
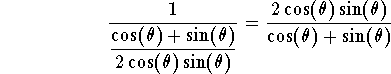
Hence
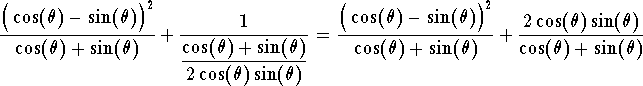
which gives
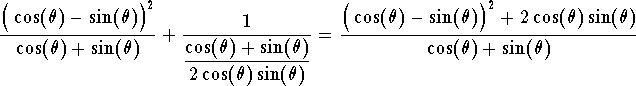
Since
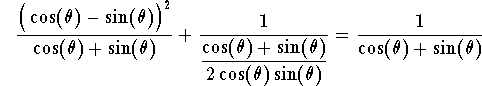
The following identities are very basic to the analysis of trigonometric expressions and functions. These are called Fundamental Identities
Reciprocal identities
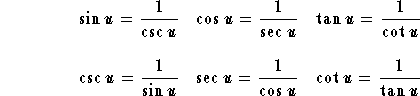
Pythagorean Identities
Quotient Identities
S.O.S.mathmatics
댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기